
Markus Lock, Head of R&D and Engineering Feintool System Parts Sachsenheim GmbH, Germany
The future of e-mobility lies in more efficient and smaller motors. Rotors and stators — the heart of a motor — play the central role in any motor design. Feintool glulock® MD (Multiple Dots) technology removes longstanding limitations on rotor and stator production, enabling more compact designs to increase the efficiency of electric motors.
E-mobility is clean, quiet and, above all, efficient. No other drive concept has such a high level of efficiency: electric cars transfer around 80 percent of the energy supplied to the road. With hydrogen drivetrain, the efficiency is only around 50 percent, and a combustion engine comes in, at best, near 40 percent. The rest of the energy is lost in the form of waste heat.
Nevertheless, electric motors still need to become more efficient. After the capacity of the battery, the energy efficiency of the motor is the most significant factor in determining the vehicle’s range. Even small increases in efficiency can deliver major improvement in range. “In the next few years, it will be a matter of exploiting those last few percent of efficiency,” says Markus Lock, Head of Engineering at Feintool.
Innovative manufacturing processes are in demand
There is room for improvement in the design of rotor and stator stacks, which together form the heart of any electric motor. In the conventional stamping and stacking process, individual laminations are joined together to form stacks using mechanical connections. However, this has disadvantages, as Markus Lock explains: “Mechanical joints always have some play. The lamellas behave like a spring, leading to a loss of performance. The deformation of the sheet metal, which is necessary for the mechanical connection, also negatively impacts efficiency.”
Joints with adhesive or bonding varnish, on the other hand, have much less of an impact on the electromagnetic properties. Thinner sheets can also be processed using this technology. While stamping stacks reach their limits at 0.3 millimeters, sheets as thin as 0.1 millimeters can be processed with adhesive or bonding. At the same time, the rotor and stator stacks become stronger and more robust. “All of the advantages of bonded design have a positive effect on motor performance,” summarizes Markus Lock.
The more efficient alternative to Backlack: glulock®
To improve electric motor efficiency, the automotive industry has increasingly turned to Backlack — a traditional secondary bonding process. The big disadvantage? It’s expensive. In addition, the process is time-consuming and energy-intense, requiring the baking varnish to be melted in an oven. Finally, electrical steel with a special coating must be used, so the material itself is also expensive.
Feintool has addressed these issues in its patented glulock® process, a more economical alternative with several benefits. As with punch stacking, the stacking process is integrated into the tool, making it very efficient. The material costs are also lower, as conventional electrical steel can be used with glulock® thanks to its application of adhesive to the metal inprocess, unlike the specialized baking varnish required in Backlack. In addition to these savings, there’s no heat required, so it’s also more sustainable. As Lock explains: “We don’t need additional energy for ovens because the glulock® process allows the packs to cure at room temperature.”
Tailor-made solutions for e-mobility
When it comes to precision, glulock® is setting new standards. “We achieve significant improvements in E-lamination stack tolerances in terms of parallelism, shape accuracy, concentricity and length tolerance,” says Lock. These improvements are the result of years of experience with adhesive packaging. The first glulock® series tool for an industrial motor was developed back in 2008. Since then, the technology has been geared towards the requirements of the automotive industry. The glulock® High Temperature (HT) process, launched in 2014, has quickly established itself in the industry. It can withstand temperatures of up to 180°C/356°F and is particularly suitable for high-speed motors.
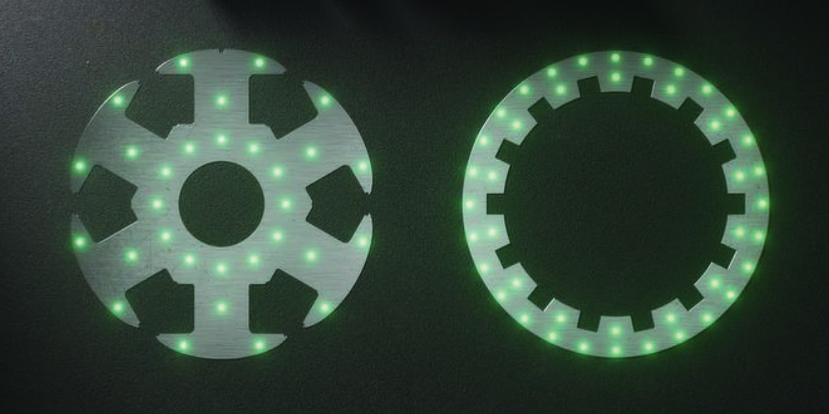
The latest development in the glulock® process is glulock® MD (Multiple Dots), and it is going to shape the next generation of electric motors. The innovative feature? Adhesive dots are no longer only applied to the yoke, but also to the teeth of the laminations. This achieves almost full-surface bonding, which makes the stacks even stronger. A US car manufacturer is already using the technology, launched in 2022, in series production. Feintool will produce a total of over 800,000 rotorstator sets by 2026. “The first automotive series order underlines the outstanding performance and potential of glulock® MD,” says Lock.
New possibilities for cooling electric motors
The glulock® MD technology also helps to solve another challenge of an electric drives: cooling. Electric motors overheat quickly, and maximum power can therefore only be delivered for a relatively short time. This becomes apparent, for example, during repeated acceleration or when driving over mountain passes. This problem is now being tackled with a completely new concept. Lock explains, “The trend is to cool electric motors from the inside, not the outside. Cooling is integrated directly into the rotors and stators.”
Integrated cooling allows the heat to be dissipated directly at the source to combat overheating. This increases motor efficiency and enables a more compact design, but requires impermeable stator and rotor stacks. “The automotive industry is currently looking for the optimum sealing method,” says Lock, “The glulock® MD adhesive packaging process is perfect for this.” The well-bonded, tight stack ensures no coolant penetrates the engine compartment. Multiple development projects are underway with manufacturers to use the Feintool glulock® MD process to make integrated motor cooling possible.
More compact design, greater efficiency
 glulock® technology is already contributing to more compact and efficient motor designs. In one development project, Feintool convinced a car manufacturer to switch from mechanical joining to glulock®. Lock explains how Feintool worked with the manufacturer to optimize the design, “We were able to save six out of a total of around 200 lamellas. That doesn’t sound like much, but if you extrapolate that across the service life and the high quantities, it’s quite significant.”
glulock® technology is already contributing to more compact and efficient motor designs. In one development project, Feintool convinced a car manufacturer to switch from mechanical joining to glulock®. Lock explains how Feintool worked with the manufacturer to optimize the design, “We were able to save six out of a total of around 200 lamellas. That doesn’t sound like much, but if you extrapolate that across the service life and the high quantities, it’s quite significant.”
The bottom line: glulock® achieves an increase in energy efficiency of up to 10 percent compared to punch stacking — the most common process in the production of rotors and stators. The iron losses caused by the build-up and continuous changes in the magnetic field can even be reduced by up to 30 percent. In this way, the innovative connection technology Feintool offers brings e-mobility closer to its ultimate goal: increased range via more efficient and compact electric motors.

Markus Lock, Head of R&D and Engineering, Feintool System Parts, Sachsenheim GmbH, Germany
About Feintool
Feintool is the international technology and market leader in electrical sheet metal stamping, fine blanking and forming. We produce highquality precision parts in large series from steel. Our customers come from automobile production, are providers of sophisticated industrial applications and operate in the energy sector. The components produced by Feintool significantly complement the megatrends for generating, storing and using green energy.
Our three core technologies are characterized by their costeffectiveness, productivity and consistently high quality. As a technology leader, Feintool is constantly expanding the limits of the production methods used and developing intelligent solutions, innovative tools and state-of-the-art manufacturing processes based on customer needs.
The company, founded in 1959 and headquartered in Switzerland, has 17 production sites in Europe, the USA, China, Japan and, from 2025, in India − with around 3,300 employees and 100 trainees. In 2023, sales amounted to 848 million Swiss francs. Feintool is listed on the stock exchange and is majority owned by the Artemis group of companies. For more information about Feintool please visit: www.feintool.com
